Identify Four Processes in Which Matter Cycles on Earth
Nitrogen cycle carbon cycle phosphorus cycle water cycle. Organisms use food molecules containing carbon as a form of energy.

Biogeochemical Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
In the biotic cycle it moves between living things and the air.

. Both processes are driven by the cycling of matter like rock magma water ice gases and living things and their remains. Chemical and Physical process. To become altered from a solid to a liquid state usually by heat.
As a result of the respiration of organisms decomposition of their bodies fermentation decay and combustion organic matter is ultimately converted into carbon dioxide or deposited in the form of sapropel humus or peat which in turn give rise to many other caustobioliths coal oil and fuel gas see Figure 2. Human activities can cause changes to these natural cycles. Molecules in the food that contain carbon transform into the organic molecules that make up the living body.
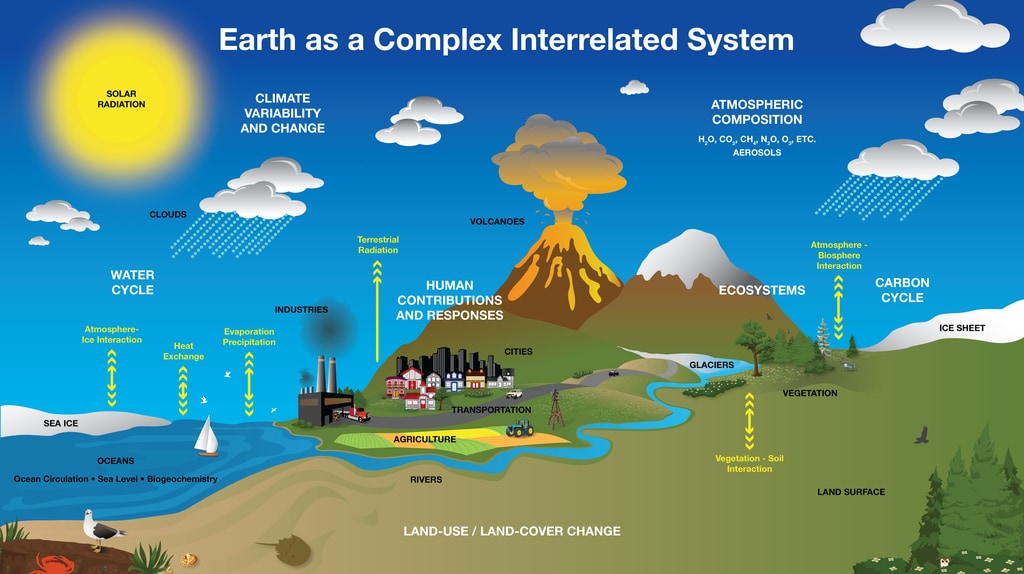
The figure below shows Earths energy budget. The water cycle carbon cycle nitrogen cycle and phosphorous cycle are the 4 types of processes that cycle matter through the biosphere. The major sources of energy in the global ecosystem are the sun and the earths interior.
Energy from the Sun is the driver of many Earth System processes. Includes volcanic eruptions the formation and breakdown of rocks and major movements of matter within and below the surface of the Earth. Carbon Cycle and Ecosystems.
Human activities can cause changes to these natural cycles. Based on the rock formations there are three basic classes which include igneous sedimentary and metamorphic. That means all the carbon hydrogen oxygen nitrogen and other elements that make up the molecules of living things have been recycled over and over throughout time.
The rock cycle and the water cycle. This research will deepen their understanding of the sub-cycles that support the global carbon cycle. In our solar system Earth is the only planet with air to breathe liquid water to drink and temperatures that are just right for life as we know it.
Carbon in the atmosphere is present in the form of carbon dioxide. It is one of the primary building blocks of all organic matter on Earth and a key element in setting Earths temperature. Examples in the Earth system include the rock cycle the food chain the carbon cycle the nitrogen cycle the water cycle and energy cycles.
Nitrogen cycle carbon cycle phosphorus cycle water cycle. There are many ways in which the energy water and biogeochemical cycles cycles of the. Natural cycles balance and regulate Earth and its atmosphere.
From the terminology itself igneous means from fire or heat. Igneous rocks form from the cooling of magma molten materials in the earths crust. Water Cycle Hydrologic.
Matter and Energy Cycles Energy Cycle. This energy flows into the Atmosphere. Carbon moves through the food chain.
Include the formation of clouds and precipitation the flow of running water and the action of lightning. Carbon is a fundamental part of the Earth system. The constant exchange of matter and energy between Earths spheres happens through chemical reactions radioactive decay the radiation of energy and the growth and decay of organisms.
The elements may differ in physical form and be either solid liquid or gaseous or they may differ in their overall form as a result of chemical reactions they have undergone. Carbon enters the atmosphere through natural processes such as respiration and industrial applications such as burning fossil fuels. By what 2 processes is water cycled from land to the atmosphere.
There are many biogeochemical cycles unified by involvement of four reservoirs of earth system through which matter cycles lithosphere rocks and soils atmosphere hydrosphere oceans surface waters groundwater glaciers biosphere living organisms matter in these reservoirs have different average times of storage or cycling. Formed from magma forced into older rocks at depths within the Earths crust which then slowly solidifies below the Earths surface. 1 Water Cycle or Hydrologic Cycle 2 Carbon-Cycle 3 Nitrogen Cycle 4 Oxygen Cycle.
In the abiotic cycle it. Earths Subsystems The four subsystems are closely linked through the biogeochemical cycleswhich involves biological geochemical and chemical factors. Scientists track the recycling of atoms through cycles called biogeochemical cycles.
As organisms eat other organisms carbon moves up the food chain. Students work in teams to research one of the three main matter and energy cycles. Some of the major biogeochemical cycles are as follows.
Carbon moves from the atmosphere to the land ocean and life through biological chemical geological and physical processes in a cycle called. Carbon Cycle on Land. This process moves matter among the four major parts of the Earth System - the atmosphere.
Life on Earth is well adapted to our planets cycles. Identify four processes in which matter and energy cycle on earth. The process of photosynthesis involves the absorption of CO 2 by plants to produce carbohydrates.
These cycles are alleyways by which substances move through biotic which is the biosphere and abiotic which is the geosphere atmosphere and hydrosphere components of Earth. Cycles of the Earth System. Closely tied to these energy sources are the two main geological processes.
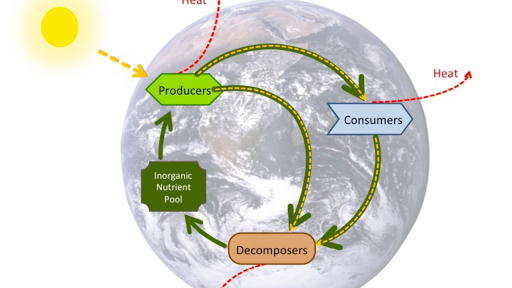
Rock formed by the cooling of magma or lava. Consequently ecologists say that matter cycles through ecosystems. Carbon moves through ecosystems in two cycles that overlap.
The water cycle the rock cycle and photosynthesis and respiration. Identify three factors that control the balance of an ecosystem. These materials get transformed into the bio mass of the producers.
Up to 24 cash back Geological process. Chemical processes and physical processes are how water is cycled from land to the atmosphere. Matter cycles The earthly cycles of water nitrogen phosphorus sulphur and carbon All elements of the periodic chart can be found on earth in many different forms.
Carbon moves back to the environment. The producers of an ecosystem take up several basic inorganic nutrients from their non-living environment. A community of organisms and the environment that the organisms inhabit.
Earth System Matter And Energy Cycles Mynasadata
Intro To Biogeochemical Cycles Article Khan Academy

Biogeochemical Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Usgs Professional Paper 1386 A Figure Gallery 1 Figure 1 Earth And Space Science Carbon Cycle Earth Science
Comments
Post a Comment